Differences Between Smart and Traditional Manufacturing

Traditional manufacturing relies on manual labor and mechanical processes with minimal automation. It operates through fixed workflows, often limiting flexibility and adaptability. In contrast, smart manufacturing embraces advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and automation to optimize production. This approach enables real-time data analysis, improving efficiency and decision-making. A study by Hanover Research revealed a 50% increase in the adoption of smart manufacturing technologies in 2021, highlighting its growing importance. Understanding these differences is crucial as industries evolve, impacting productivity, workforce dynamics, and global competitiveness.
Key Takeaways
Smart manufacturing leverages advanced technologies like IoT and AI to enhance efficiency and decision-making, leading to faster production cycles.
Traditional manufacturing excels in producing standardized products but lacks the flexibility and adaptability needed to respond to market changes.
Investing in smart manufacturing can lead to significant cost savings through optimized resource utilization and reduced downtime.
The transition to smart manufacturing requires a skilled workforce; companies should prioritize training and upskilling to meet new technological demands.
Sustainability is a key benefit of smart manufacturing, as it minimizes waste and promotes environmentally friendly practices.
Embracing smart manufacturing positions industries to innovate and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Balancing traditional and smart manufacturing approaches can help businesses address diverse production needs while navigating workforce transitions.
Key Features of Traditional Manufacturing
Characteristics of Traditional Manufacturing
Traditional manufacturing relies on manual labor and mechanical processes. It often uses subtractive methods, where raw materials like metal, wood, or plastic are shaped by removing excess material through machining, grinding, or drilling. Processes such as molding, forming, and joining play a central role in production. These methods emerged during the First Industrial Revolution, which introduced mechanization and steam power to enable mass production. Traditional manufacturing typically follows fixed workflows, making it less adaptable to changes in demand or design.
Strengths of Traditional Manufacturing
Traditional manufacturing offers several advantages. It excels in producing standardized products at scale, thanks to techniques like interchangeable parts and assembly lines. These methods ensure consistency and reliability in output. The simplicity of traditional systems reduces the need for advanced technical expertise, making them accessible to a broader workforce. Additionally, the use of well-established processes ensures durability and precision in many industries, particularly those requiring heavy machinery or large-scale production.
Limitations of Traditional Manufacturing
Despite its strengths, traditional manufacturing faces notable challenges. Its reliance on manual labor and fixed workflows limits flexibility and scalability. Adapting to new designs or market demands often requires significant time and resources. The subtractive nature of its processes generates considerable material waste, impacting cost efficiency and sustainability. Furthermore, traditional systems lack real-time monitoring and data-driven decision-making, which can lead to inefficiencies and slower response times to disruptions. These limitations highlight the need for more innovative approaches in modern manufacturing landscapes.
Key Features of Smart Manufacturing
Characteristics of Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing integrates advanced technologies to enhance production processes. It relies on interconnected systems, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing, to collect and analyze data in real time. These technologies enable manufacturers to monitor operations, predict maintenance needs, and optimize workflows. Unlike traditional methods, smart manufacturing emphasizes flexibility and customization. It allows factories to adapt quickly to changing market demands or product designs. This approach fosters a data-driven environment where decisions are based on insights rather than assumptions.
The use of automation plays a significant role in smart manufacturing. Robots and automated machinery handle repetitive tasks with precision, reducing human error and increasing efficiency. Digital twins, which are virtual replicas of physical assets, simulate production scenarios to identify potential issues before implementation. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and enhances productivity. By leveraging these tools, smart manufacturing creates a seamless connection between physical and digital operations.
Benefits of Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing offers numerous advantages that transform the production landscape. One of its primary benefits is improved efficiency. Real-time data analysis identifies bottlenecks and inefficiencies, enabling swift corrective actions. This results in faster production cycles and reduced operational costs. Additionally, the ability to predict equipment failures through predictive maintenance minimizes unplanned downtime, ensuring consistent output.
Another key benefit is enhanced product quality. Smart manufacturing systems monitor every stage of production, ensuring adherence to quality standards. Automated inspections detect defects early, reducing waste and rework. Furthermore, the flexibility of smart manufacturing allows for greater customization. Manufacturers can produce small batches of personalized products without compromising efficiency, meeting diverse customer needs.
Sustainability also stands out as a significant advantage. By optimizing resource usage and minimizing waste, smart manufacturing supports environmentally friendly practices. Energy-efficient technologies and precise material management contribute to reduced carbon footprints. This aligns with global efforts to promote sustainable industrial growth.
Challenges of Smart Manufacturing
Despite its benefits, smart manufacturing presents several challenges. The initial investment required for implementing advanced technologies can be substantial. Many manufacturers face difficulties in upgrading legacy systems to integrate with modern solutions. This transition often demands significant time and resources, posing a barrier for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Data security emerges as another critical concern. The reliance on interconnected systems increases vulnerability to cyberattacks. Manufacturers must implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information and maintain operational integrity. Additionally, the complexity of smart manufacturing systems requires a skilled workforce. Training employees to operate and maintain these technologies becomes essential, yet it can be a time-intensive process.
Adapting to rapid technological advancements also poses a challenge. Manufacturers must continuously update their systems to remain competitive, which can strain budgets and resources. Despite these obstacles, the long-term benefits of smart manufacturing often outweigh the initial difficulties, making it a worthwhile investment for forward-thinking industries.
Direct Comparisons Between Traditional and Smart Manufacturing
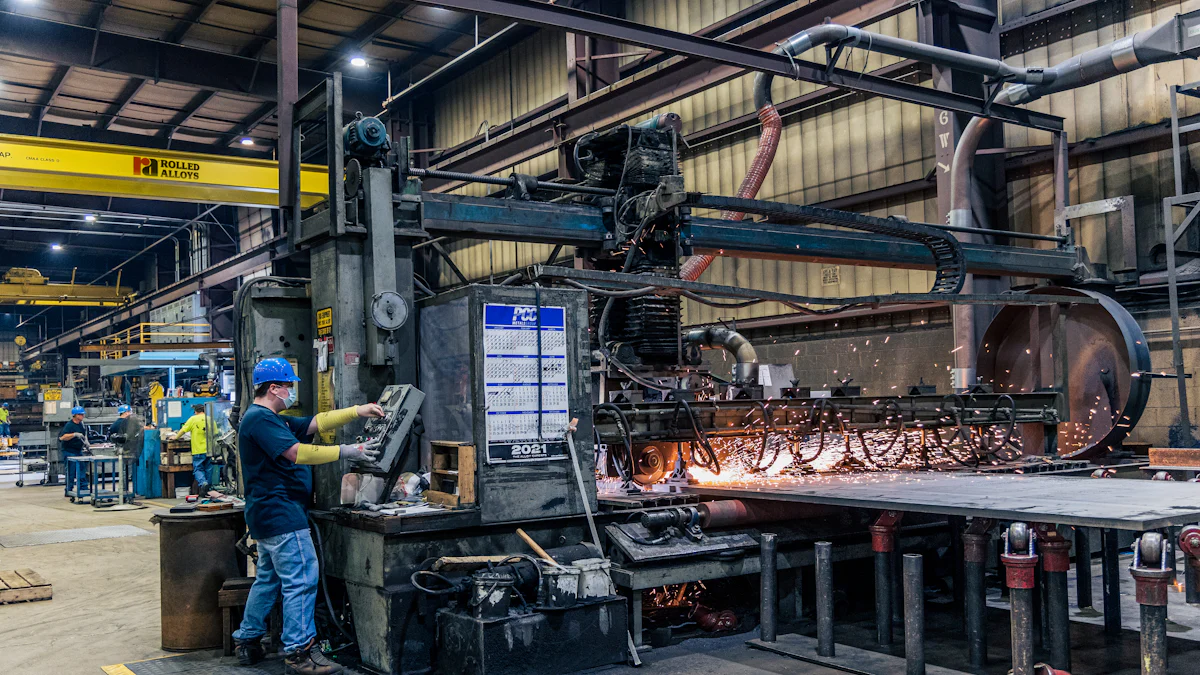

Efficiency and Productivity
Efficiency and productivity serve as critical benchmarks in manufacturing. Traditional manufacturing often relies on manual labor and fixed workflows, which can slow production cycles. Workers perform repetitive tasks, and the lack of real-time monitoring can lead to delays in identifying and resolving inefficiencies. This approach limits the ability to optimize processes dynamically.
In contrast, smart manufacturing leverages advanced technologies to enhance efficiency. Real-time data analysis identifies bottlenecks and streamlines operations. Automated systems, such as robotics and AI-driven tools, execute tasks with precision and consistency. A report highlighted that smart manufacturing technologies can boost productivity for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) by 7% to 50%. This significant improvement underscores the transformative potential of adopting a technology-driven approach.
Cost Implications
Cost considerations play a pivotal role in determining the viability of manufacturing methods. Traditional manufacturing often incurs higher operational costs due to its reliance on manual labor and material-intensive processes. The subtractive nature of traditional methods generates waste, increasing material expenses. Additionally, downtime caused by equipment failures or inefficiencies further escalates costs.
Smart manufacturing, on the other hand, offers cost-saving opportunities through optimized resource utilization. Predictive maintenance reduces unplanned downtime, minimizing repair expenses. Automation decreases reliance on manual labor, lowering long-term operational costs. Although the initial investment in smart manufacturing technologies can be substantial, the long-term savings often outweigh these upfront expenses. The shift to smart manufacturing represents a cost-efficient path for industries aiming to remain competitive in a dynamic market.
Scalability and Adaptability
Scalability and adaptability determine how well a manufacturing system responds to changing demands. Traditional manufacturing operates within rigid frameworks, making it challenging to scale production or adapt to new designs. Adjustments often require significant time and resources, hindering responsiveness to market fluctuations.
Smart manufacturing excels in scalability and adaptability. Interconnected systems and data-driven insights enable manufacturers to adjust production levels swiftly. Customization becomes feasible without compromising efficiency, allowing businesses to cater to diverse customer needs. The flexibility of smart manufacturing ensures that industries can respond effectively to evolving market trends. This adaptability positions smart manufacturing as a forward-thinking solution for modern production challenges.
Workforce Impact
The shift from traditional to smart manufacturing significantly influences the workforce. Traditional manufacturing relies heavily on manual labor, requiring workers to perform repetitive tasks. This approach often demands physical endurance and basic technical skills. However, it limits opportunities for skill development and career progression. Workers in traditional setups face challenges adapting to new roles as industries evolve.
Smart manufacturing introduces a transformative impact on workforce dynamics. Advanced technologies like automation, IoT, and AI reduce the dependency on manual labor. Instead, they create demand for highly skilled professionals capable of managing and maintaining these systems. Workers must acquire expertise in areas such as data analysis, robotics, and system integration. This transition fosters a more knowledge-driven workforce, emphasizing continuous learning and adaptability.
A report highlighted that smart manufacturing technologies can boost productivity for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) by 7% to 50%. This productivity surge underscores the importance of equipping the workforce with relevant skills to harness these advancements effectively.
The adoption of smart manufacturing also reshapes job roles. Routine tasks previously performed by humans are now automated, allowing employees to focus on strategic and creative responsibilities. This shift enhances job satisfaction and opens avenues for innovation. However, it also presents challenges, particularly for workers in traditional roles who may struggle to adapt to the technological demands of smart manufacturing.
To address these challenges, industries must invest in workforce training and development. Upskilling programs and partnerships with educational institutions can bridge the gap between existing skills and emerging requirements. By fostering a culture of learning, organizations can ensure a smooth transition for their workforce while maximizing the benefits of smart manufacturing.
Implications for the Future
Industry Transformation
The manufacturing industry is undergoing a profound transformation driven by technological advancements. Smart manufacturing plays a pivotal role in this shift by integrating data-driven processes and automation. This approach enhances operational efficiency and enables manufacturers to respond swiftly to market demands. A survey revealed that 83% of manufacturers believe accelerating the adoption of smart manufacturing is essential. This statistic underscores the urgency industries feel to modernize their operations and remain competitive.
The integration of smart manufacturing technologies fosters innovation across various sectors. Companies can now experiment with new production methods, such as additive manufacturing, to create complex designs with minimal waste. Interconnected systems also promote collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, streamlining supply chains. As industries embrace these changes, they position themselves to meet the challenges of a rapidly evolving global market.
Workforce Evolution
The adoption of smart manufacturing significantly impacts workforce dynamics. Advanced technologies reduce the reliance on manual labor, shifting the focus to roles requiring technical expertise. Workers must develop skills in areas like robotics, data analysis, and system integration to thrive in this new environment. According to a report, 94% of manufacturers plan to maintain or expand their workforce due to smart manufacturing adoption. This statistic highlights the potential for job growth despite concerns about automation replacing traditional roles.
Upskilling programs and educational partnerships play a crucial role in preparing the workforce for these changes. Companies invest in training initiatives to bridge the gap between existing skills and emerging requirements. This approach not only ensures a smooth transition but also fosters a culture of continuous learning. By equipping employees with the necessary tools, industries can harness the full potential of smart manufacturing while supporting workforce development.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Sustainability has become a critical consideration for modern industries. Smart manufacturing addresses this need by optimizing resource usage and minimizing waste. Technologies like IoT and AI enable real-time monitoring of energy consumption, allowing manufacturers to identify inefficiencies and implement corrective measures. This proactive approach reduces carbon footprints and supports environmentally friendly practices.
The shift to smart manufacturing also promotes the use of renewable energy sources. Factories can integrate solar panels, wind turbines, and other sustainable solutions into their operations. Additionally, advanced recycling techniques ensure that materials are reused effectively, further reducing environmental impact. These efforts align with global initiatives to combat climate change and promote sustainable industrial growth.
By embracing smart manufacturing, industries not only enhance their operational efficiency but also contribute to a greener future. This dual benefit positions smart manufacturing as a key driver of sustainable development in the 21st century.
Traditional manufacturing and smart manufacturing represent two distinct approaches to production, each with unique strengths and challenges. Traditional methods excel in simplicity and reliability but often lack flexibility and efficiency. Smart manufacturing, driven by advanced technologies, optimizes processes, enhances scalability, and supports sustainability. Balancing these approaches allows industries to address diverse needs while navigating workforce transitions and market demands.
As manufacturing evolves, businesses adopting smart manufacturing will gain a competitive edge, addressing challenges like skilled labor shortages and complex supply chains. This evolution underscores the transformative potential of technology in shaping a sustainable and innovative future for industries.
See Also
Innovative Advances in Huizhou Zhongkai Tech Area
Unveiling Creativity in Zhongkai High-tech District
Leading Figures in the Worldwide Smart Control Sector
Zhongkai Tech Zone: Center for Intelligent Terminal Developments
Zhongkai High tech Zone National foreign trade transformation and Upgradi Base(Electronic Information)Cloud Platform.
Address: Zhongkai High-tech Zone,Huizhou City ,Guangdong,China
E-mail: huizhoueii@163.com 13510001271@163.com
Tel: +86-0752-3279220 Mobile: +86-13510001271


